“The Rise of Agentic Automation as a Structural Inflection: Recalibrating Governance and Capital in the Autonomous Enterprise Era”
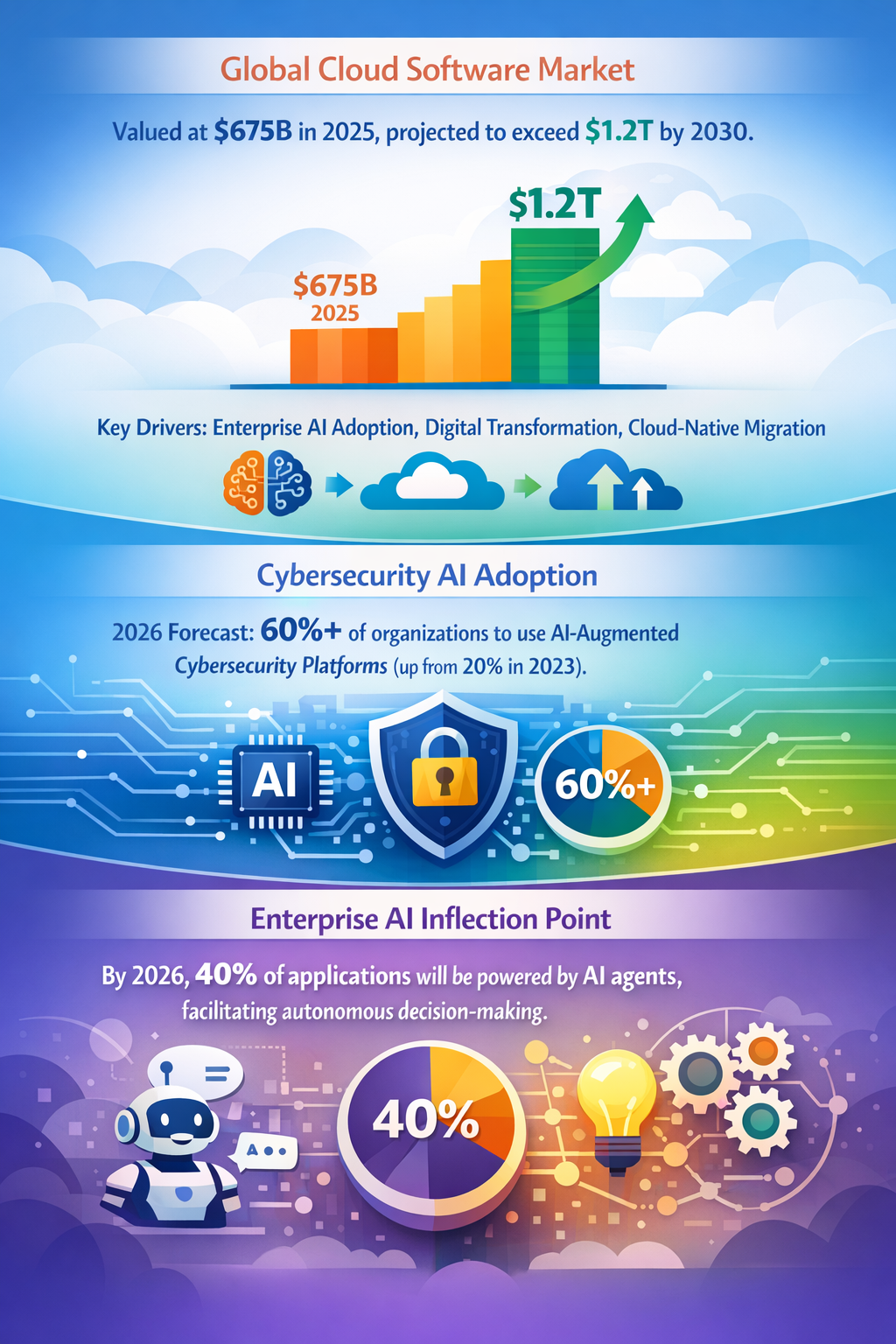
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is on the cusp of a material transformation from tool-assisted automation to autonomous agentic systems capable of independent decision-making. While this transition is broadly anticipated, a less recognized but critically consequential weak signal is the emergent shift toward “agentic automation” in enterprises—AI agents operating across critical applications without human intermediaries. This development, projected to exceed 40% penetration in enterprise applications by 2026–2027, is poised to trigger structural changes affecting capital allocation, regulatory frameworks, industrial dynamics, and risk governance over the coming 5–20 years.
Signal Identification
This phenomenon qualifies as an emerging inflection indicator rather than a diffuse trend or isolated innovation, because it represents a capability threshold crossing—from AI as a decision-support tool to AI as autonomous actor within operational and strategic domains. The 5–10 year time horizon is supported by multiple projections forecasting nearly 40% enterprise penetration of agentic AI by 2026–2027 (Joget, 2026; ETEdge Insights, 2026). The plausibility band is high, given convergent investment, adoption momentum, and institutional pilot programs. Key affected sectors extend beyond tech and manufacturing into financial services, cybersecurity, supply chain management, and public infrastructure planning.
What Is Changing
The provided sources document a rapid escalation in AI-powered automation adoption in enterprises and manufacturing, with manufacturers expecting to more than double their use of AI-enabled automation by 2030 (Yahoo Finance, 2023). More notably, agentic AI agents—software entities that can independently initiate, monitor, and adjust workflows—are moving into nearly 40% of enterprise application footprints by mid-decade (Joget, 2026; ETEdge Insights, 2026). This crosses a threshold from supporting human decision-making towards autonomous operational governance.
A consistent theme is that these AI agents not only automate routine tasks but begin exercising judgment capacities and risk assessments in real time. For instance, European banks have begun deploying machine learning to rank risk drivers with textual explanations for human investigators, aligning with regulatory expectations (Compliance Digest, 2026). This highlights a critical evolution: AI agents are increasingly embedded within regulated risk governance frameworks, blurring accountability lines.
Furthermore, the growth of AI in customer engagement—such as AI managing over 15% of call center interactions by 2026 (Precedence Research, 2024)—demonstrates scaling in front-line autonomous decisioning. Complementary to this, emergent regional AI hubs like India's Dholera project signal state-driven infrastructural investments in AI ecosystems expected to anchor sustainable digital operations by 2028 (Bankers Adda, 2026).
These advances in agentic AI surpass incremental automation. They introduce autonomous actors capable of decision iteration unseen in prior robotics or rules-based systems. This creates systemic conditions for operational decentralization and elevates the importance of machine-driven governance models within firms and, potentially, regulatory regimes.
Disruption Pathway
The escalation of agentic automation will unfold as enterprises seek productivity gains while mitigating growing complexity and risk in digital operations. Amplifiers include competitive pressure to adopt autonomous agents for faster, data-driven decision cycles, and the proliferation of cloud-based AI infrastructure lowering deployment thresholds. Regulatory adjustments recognizing AI’s role in decision-making—for instance, Europe’s Machine Readability of AI Risk Drivers (Compliance Digest, 2026)—may incentivize firms to embed these technologies for enhanced regulatory compliance agility.
However, embedding autonomous agents across critical applications generates novel stresses: accountability ambiguity for AI-driven decisions, increased systemic exposure to AI errors or adversarial manipulation, and concentration risks as third-party AI providers dominate. This may degrade traditional governance structures designed for clear human oversight and legal liability chains, forcing reconfiguration.
Consequently, organizations and regulators may be compelled to develop “AI governance frameworks” internal to operating models—formalizing continuous AI system validation, ethical audits, and human-agent collaboration protocols. Fiscal capital allocation will shift towards integrated AI risk management and compliance capabilities rather than solely development or deployment, altering industrial cost bases and value chains (Finextra, 2023).
Over extended timeframes (10–20 years), these dynamics could reshape dominant industry structures by privileging ecosystems capable of embedding, governing, and certifying autonomous AI agents at scale. Capital access may correlate with demonstrable AI governance maturity, while regulatory bodies could require auditability and ‘explainability’ of autonomous decision pathways as licensing preconditions. This systemic adaptation shifts beyond technology adoption to a new institutional order for AI responsibility and control.
Why This Matters
For senior decision-makers, recognizing this inflection is vital for aligning capital allocation strategies to the emergent operational realities of agentic automation. Investment portfolios emphasizing AI integration should elevate governance and risk assurance capabilities, anticipating possible shifts in regulatory compliance costs and operational resilience demands.
Regulators must proactively develop frameworks that assign liability between human overseers, autonomous AI agents, and service providers to prevent systemic governance gaps. Industrial strategies may need to balance AI agent deployment with workforce and societal impacts, as autonomous decisioning redefines roles and competitive advantages.
Supply chains will increasingly rely on AI-mediated, cross-organizational coordination, exposing assets and data to new vulnerabilities but also enabling unprecedented operational velocity. This changes how supply chain resilience and cybersecurity are prioritized and resourced.
Implications
The expansion of agentic automation may lead enterprises to restructure around AI-centric operational models that prioritize continuous autonomous decisioning, with AI governance infrastructures integrated into core functions. This could increase barriers to entry for firms unable to achieve necessary AI risk management maturity, thereby consolidating competitive dynamics toward technologically adept incumbents or ecosystems.
Conversely, failure to properly govern agentic systems might expose organizations to reputational, legal, and operational risks that undermine trust and financial stability. Some interpretations may mistake this signal as a simple scale-up of AI tools without appreciating the governance transformation required, leading to underinvestment in critical risk control infrastructure.
Importantly, this development is not equivalent to generalized AI hype or utopian autonomy where AI replaces humans entirely. Instead, it reflects a nuanced shift: enterprises delegating increasing autonomous agency to AI within clearly defined risk and regulatory boundaries, sparking evolution in operational and governance paradigms.
Early Indicators to Monitor
- Growth in procurement and deployment of agentic AI platforms explicitly designed for autonomous decision workflows within enterprises.
- Rising inclusion of AI explainability and accountability requirements in regulatory drafts, supervisory guidelines, or industry codes of practice.
- Clustering of venture funding toward AI governance startups providing risk auditing, bias detection, and decision traceability tools.
- Public-private collaborations establishing standard frameworks or certifications for autonomous AI agent operations.
- Increasing disclosure from regulated entities on AI agent usage in compliance or risk functions.
Disconfirming Signals
- Regulatory frameworks imposing severe restrictions or bans on autonomous decision-making by AI in critical sectors.
- Technological stagnation or failures in AI agent interoperability and robustness preventing scaling beyond pilot projects.
- Widespread negative incidents causing reputational damage and a retrenchment from AI autonomy in enterprises.
- Persistent legal ambiguities blocking assignment of liability for AI-driven decisions, resulting in systemic adoption paralysis.
- Emergence of alternative automation paradigms emphasizing tightly coupled human-machine collaboration rather than agentic autonomy.
Strategic Questions
- How will current capital deployment priorities shift to incorporate AI governance and risk management as core enterprise capabilities?
- What regulatory frameworks are needed to clarify accountability and liability in autonomous AI-driven decision-making?
- How will industrial structures evolve to privilege firms or ecosystems capable of embedding and governing agentic AI at scale?
- What new resilience and cybersecurity models must be developed to manage systemic risks introduced by widespread agentic automation?
- How can organizations balance human oversight with AI autonomy to optimize performance while maintaining trust and compliance?
- To what extent should governments invest in regional AI infrastructure hubs to catalyze ecosystem readiness for agentic automation?
Keywords
Agentic Automation; Autonomous AI; AI Governance; Risk Management; Capital Allocation; Regulatory Frameworks; Industrial Structure; Machine Learning Explainability; AI Ecosystems; Operational Resilience.
Bibliography
- Joget, AI Agent Adoption in 2026 15/05/2026
- ETEdge Insights, Enterprise AI in 2026 04/01/2026
- Yahoo Finance, Automation in Manufacturing by 2030 18/01/2023
- Compliance Digest, ML in Banking Risk Governance 23/09/2026
- Precedence Research, AI in Call Centers 06/03/2024
- Bankers Adda, Dholera AI Infrastructure Project 21/02/2026
- Finextra, AI as Disciplined Enterprise Investment 12/11/2023